The poor living conditions that many of the children at Stannington Sanatorium came from, outlined in our last post, can often leave physical markers on the skeleton, namely Harris Lines.
Harris Lines are an indication of periods of arrested growth whilst the body is still growing during childhood and can be displayed as opaque, transverse lines on long bones. These can be identified through radiographic imaging or physically on skeletal remains.
The appearance of these lines is considered to show periods in an individual’s childhood when the body comes under stress, which is usually attributed to malnutrition or significant childhood disease. In order for the individual to acquire Harris Lines, they have to have recovered from the period of stress, prolonged malnutrition or disease would not result in their appearance.
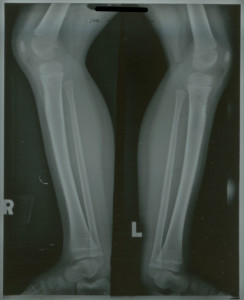
Numerous patients from Stannington Sanatorium demonstrate Harris Lines in their radiographs. One such example is seen above, patient 148/1948. Thi image was taken in November 1948, approximately 10 months after initial diagnosis of tuberculosis was made. On this patient Harris Lines are identifiable on both proximal and, to a greater degree, distal tibiae, as a brighter, opaque line close to the epiphysis.
This individual was admitted to the sanatorium aged 2 with a Primary Complex, primary infection in the mid zone of the right lung. Their medical history indicates that their father had been diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and subsequently died. The family, consisting of mother, father and two children were living in one room for the majority of the individual’s life, only moving to a two roomed house around the time of their admission to Stannington and on admittance to the sanatorium the child was described in the medical notes as being ‘thin’ and ‘ pale’.
Social conditions such as these would have attributed to the premise of the child undergoing one or more periods of stress during growth and alongside the description of the individual being ‘thin’, malnutrition is possible. A poor appetite or anorexia is often noted in the medical notes of patients as being symptomatic of tuberculosis, again suggesting possible malnutrition. However, the effects of the tuberculosis infection alone would have put the body under due stress and may, therefore, have contributed to the presence of Harris Lines. Both malnutrition and acute tuberculous infection are potential causes of the Harris Lines, alone and in conjunction with one another, and demonstrate the secondary effects that disease and social conditions can have on an individual’s body.
This patient was removed against medical advice approximately one month after admittance, only to be re-admitted seven months later with tuberculosis of the cervical vertebrae. They were eventually discharged in December 1950, two years later, but continued to be seen as an out-patient. No further treatment was required at Stannington Sanatorium.
For more radiographic images, view the ‘Radiographs from Stannington’ on Flickr https://www.flickr.com/photos/99322319@N07/sets/72157648833066476/
Sources
Roberts, C and Manchester, K (2006). Archaeology of Disease (3rd Edition). Cornell University Press.

This i a typical case of Harris’ lines, obviously due to a combination of malnutrition and tuberculosis initiated about 1 year earlier. Vide: Holck P. Harris’ linjer. Tidsskr Nor Lægeforen nr. 15, 1984, 104, 1028-31.